Grave- This is the articulation of the hip joint.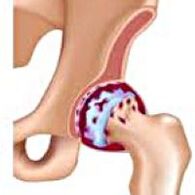 It has gradually developed, for several years, prone to evolution, it can be one and double and double.It is accompanied by pain and restriction of joint movements.In the later stages, hip muscle atrophy and a decrease in edge.The diagnosis is determined on the basis of clinical symptoms and the effects of radiography.In the early stages of carxar, conservative treatment.By destruction of the joint, especially in young and middle -aged patients, surgery (intra -protective) is indicated.
It has gradually developed, for several years, prone to evolution, it can be one and double and double.It is accompanied by pain and restriction of joint movements.In the later stages, hip muscle atrophy and a decrease in edge.The diagnosis is determined on the basis of clinical symptoms and the effects of radiography.In the early stages of carxar, conservative treatment.By destruction of the joint, especially in young and middle -aged patients, surgery (intra -protective) is indicated.
General information
Coconstruction (osteorania or deformation of hip arthritis) is a degenerative dystrophic disease.It usually develops at the age of 40 and older.It can be the result of various injuries and common diseases.Sometimes it happens for no apparent reason.Coksarrosis is characterized by a gradual progressive course.In the early stages, conservative treatment methods are used.In the later stages, the function of the common function can only be restored functional.
In orthopedics and traumatic, coxordinia is one of the most common articles.The high frequency of its growth is due to a significant load on the hip joint and the widespread prevalence of congenital pathology - the malformation of the joints.Women suffer from Coksarrosis a little more often than men.
The causes of gracking
Primary (resulting for unknown reasons) and secondary (developed as a result of other diseases) joints of the hip joint are distinguished.
Secondary Coksarrosis may be the result of the following diseases:
- Hip joint dysplasia.
- Inherent dislocation of the thigh.
- Pertes diseases.
- Aseptic necrosis of the thigh head.
- Infectious lesions and inflammatory processes (for example, arthritis of the hip joint).
- Injuries (traumatic outbreaks, hip fractures, pelvic fractures).
Coksarrosis can be either one or double.With primary coating, there is often often observed a simultaneous spine damage (osteochondria) and knee joint (knee).
Risk factors
Among the factors that increase the likelihood of the development of the conscience include:
- Fixed increased load on the joint.They are often observed in athletes in people with excess body weight.
- Traffic disorders, hormonal changes, metabolic disorders.
- Spine pathology (rolling, scoliosis) or stop (flat legs).
- Elderly and old.
- A sedentary lifestyle.
Coksarrosis itself is not inherited.However, certain characteristics (metabolic disorders, structural characteristics of the skeleton and cartilage weakness) can be inherited by the child by parents.Therefore, in the presence of relatives of blood suffering from crothery, the likelihood of the disease is slightly increased.
Potato
The hip joint is formed by two bones: ileum and femoral.The head of the thigh is articulated with the rattling of the hare bone, forming a peculiar "hinge".During the movements, the acetabular remains stationary and the femoral head moves in various directions, ensuring the bending, expansion, abduction, appearance and rotary hips.
During the movements, the articular surfaces of unhindered bone transparency in relation to each other, thanks to the smooth, elastic and durable hyaline cartilage covering the cavity of the rotational cavity and the head of the thigh.In addition, the glazed cartilage performs a shock function -supplying and involved in the redistribution of the load during movement and walking.
In the hinge cavity there is a small amount of liquid joint, which plays the role of lubrication and provides a vitreous cartilage diet.The joint is surrounded by a dense and strong capsule.Above the capsule are large femoral and gluten muscles, which provide joint movements and, along with a honder cartilage, are also shock absorbers that protect the joint from unsuccessful movements.
With cochimia, the joint of the joint becomes thicker and more viscous.The surface of the glass cartilage dries, loses smoothness, covered with cracks.Due to the resulting roughness, the cartilage is constantly injured during the movements, which causes them to dilute them and worsens the pathological changes in the joint.As the trunk evolves, the bones begin to deform, "adjusting" to increased pressure.The metabolism in the joint is deteriorating.In the subsequent stages of corrosion there is severe atrophy of the muscles of the painful limb.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of the disease include joint pain, groin region, thigh and knee joint.Also, with the costume, stiffness of the movements and the rigidity of the joint, the gait disorder, the atrophy, the atrophy of the hip muscles and the reduction of the limb on the side of the damage.A characteristic feature of Coksarrosis is a limit to the abduction (for example, the patient is difficult when trying to sit on a chair).The presence of certain points and their severity depends on the stage of the carxar.The first and most stable symptom is pain.
ToGrade 1Patients complain about periodic pain, which occurs after physical activity (running or prolonged walking).Pain is located in the joint, less frequently on the thigh or knee.After rest, it usually disappears.The walking for the 1st degree trunk is not broken, the movements are fully maintained, there is no muscle atrophy.
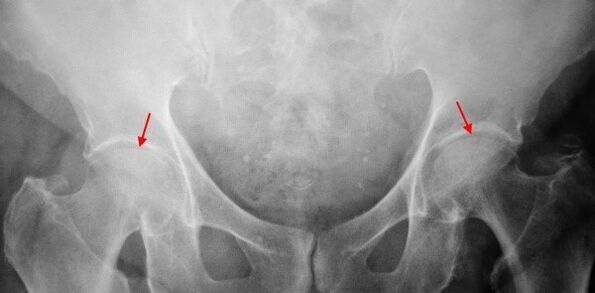
Concerning the X - -caring of the patient suffering from first -degree grining, mild changes are determined: moderately uneven stenosis of the joint gap, as well as bone developments around the outer or inner edge of the acetabular absence of changes from the head and neck of the bone.
To2 pointsPain becomes more severe, often occurs in a state of rest, radiates in the thigh and the groin.After significant physical activity, the patient with coksarrosis begins to limp.The volume of joint movements decreases: abduction and internal thigh rotation is limited.
In pictures X for the 2nd degree body, a significant heterogeneous narrowing of the joint gap is determined (more than half of the normal height).The femoral head is somewhat shifted upwards, deformed and increases in size and its contours become heterogeneous.Bone increases with this degree of trunk occur not only on the inside but also on the outer edge of the acetabular and to get out of the cartilage.
To3 pointsPain becomes constant, patients' concern not only during the day, but also at night.Walking is difficult when moving, a patient with Coksarrosis is forced to use a cane.The volume of joint movements is strongly limited, the muscles of the buttock, the hips and the lower legs are atrophic.The inability to remove the thigh muscles becomes the cause of the divergence of the pelvis at the front level and the limb of the limb on the painful side.In order to compensate for the shortcut, a patient suffering from grains, when walking, leans the body in the painful direction.Because of this, the center of gravity shifts, the load on the painful joint increases sharply.
In the 3rd degree x -rays for the 3rd degree body, a sharp narrowing of the joint gap, a strong extension of the thigh head and multiple bone increases are detected.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of carxars is based on clinical symptoms and data of additional studies, the main of which is radiography.In many cases, the X -rays make it possible to establish not only the grade of the trunk but also the cause of its appearance.Thus, for example, the increase in the corner-corner angle of the throat, scenes and leveling of the acetabular indicate malformation and changes in the shape of the near part of the thigh indicate that grains is a consequence of peeres or youthful disease.In radiographs of patients with crothaul, changes that indicate injuries may also be detected.
As other methods of organic diagnosis of trunk, CT and magnetic resonance imaging can be used.Computed tomography allows you to study in detail the pathological changes with bone structures and magnetic resonance imaging provides the opportunity to evaluate soft tissue disorders.
Diagnosis
First of all, coachartia should be differentiated from rage (knee joints) and spine osteochondria.Muscle atrophy, which occurs in 2 and 3 stages of corrosion, can cause knee joint pain, which are often more brighter than pain in the area of lesion.Therefore, with the patient's complaints about knee pain, a clinic (inspection, palpation, tumor tumor) is the study of hip joints and, if suspected of drilling, direct the patient to radiography.
Pain for radical syndrome (nerve root compression) for osteochondria and some other diseases of the spine can mimic pain with mockery.Unlike Coksarrosis, when pressing the roots, the pain suddenly occurs, after an unsuccessful movement, a sharp turn, the lifting weights, etc., is placed in the buttocks and spreads along the back of the thigh.A positive symptom of intensity is detected - severe pain when the patient tries to increase a straightening end, located on his back.At the same time, the patient freely takes his foot to the side, while in patients with coksarrosis, abduction is limited.It should be borne in mind that osteochondria and bumping can be observed simultaneously, therefore, in all cases, a thorough examination of the patient is necessary.
In addition, Cokesarrosis is differentiated by a boot boot boots - aseptic inflammation in the field of muscle gluttony adhesion.Unlike babyemia, the disease develops rapidly within 1-2 weeks, usually after injury or significant physical activity.Pain intensity is higher than with Coksarrosis.Movement restrictions and limb reduction are not observed.
In some cases, with an informal course of the disease or reactive arthritis, symptoms that resemble understanding may be observed.Unlike babyia, with these diseases, the top of the pain falls at night.Pain syndrome is very severe, it can be reduced when walking.The morning stiffness is characteristic, which occurs immediately after awakening and gradually disappears within a few hours.
Courier treatment
The treatment of pathology deals with orthopedists.The choice of treatment methods depends on the symptoms and stage of the disease.In the 1 and 2 stages of the carxar, conservative treatment is performed.During the deterioration period of the trunk, an injection block is used, non -essential anti -inflammatory drugs are used (pyroxia, indomethacin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, etc.).It should be borne in mind that the medicines in this group are not recommended for a long time, as they can have a negative effect on the internal organs and suppress the ability of the hyaline cartilage to restore.
To restore the damaged cartilage for granted, funds are used by a group of chondroprotectorates (chondroitin sulfate, cartilage extract, etc.).To improve blood circulation and eliminate small vessel convulsions, vasodilator drugs (zinnisine, nicotine, pentohefiline, nicotinic xanthinol).According to indications, muscle relaxation (muscle relaxation drugs) are used.
With persistent pain syndrome, patients suffering from coksarrosis can prescribe intra -mararmatic injections using hormonal drugs (hydrocortisone, triamkinolone, metrumor).Steroid therapy should be carried out with caution.In addition, with a trunk, local products are used - heating ointments that do not have a strong therapeutic effect, however, in some cases relieve muscle spasm and reduce pain due to their "fragmentary" effect.Also, with groxare, physiotherapeutic processes are prescribed (luminous, ultrasonic treatment, laser treatment, UHF, induction, magnetotherapy), massage, manual therapy and therapeutic gymnastics.
The diet for Coksarrosis does not have an independent therapeutic effect and is used only as a means of weight loss.The reduction in body weight allows you to reduce the load on hip joints and, therefore, to facilitate the course of Coksarrosis.In order to reduce the load on the joint, the doctor, depending on the degree of trunk, may recommend walking with cane or crutches.
In the later stages (with 3rd degree purses), the only effective method of treatment is function - replacing the damaged hinge.Depending on the nature of the damage, it can be used can be used either a city single (replacing only the head of the thigh) or two poles (replacing both the head of the thigh and the rotating cavity).
The operation of the coxartes lunatic is a programmed, after full examination, under general anesthesia.During the postoperative period, antibiotic therapy is performed.The seams are removed at 10-12 days, after which the patient is prescribed for the treatment of external patients.After the impact, the rehabilitation measures are necessarily maintained.
In 95% of cases, surgical intervention to replace the joint with a crothery ensures complete restoration of the limbs.Patients can operate, move actively and even play sports.The average life span of intent, subject to all recommendations, is 15-20 years.After that, a second function is required to replace a worn -out stent.